Create an AI agent with a custom frontend
Squid lets you create unique user experiences using Squid AI. Follow along to create an AI agent that answers questions about squids!
What you'll build
- A custom AI agent run in a React frontend application with a unique knowledge base
Environment setup
- In the Squid Console, switch to the
devenvironment.
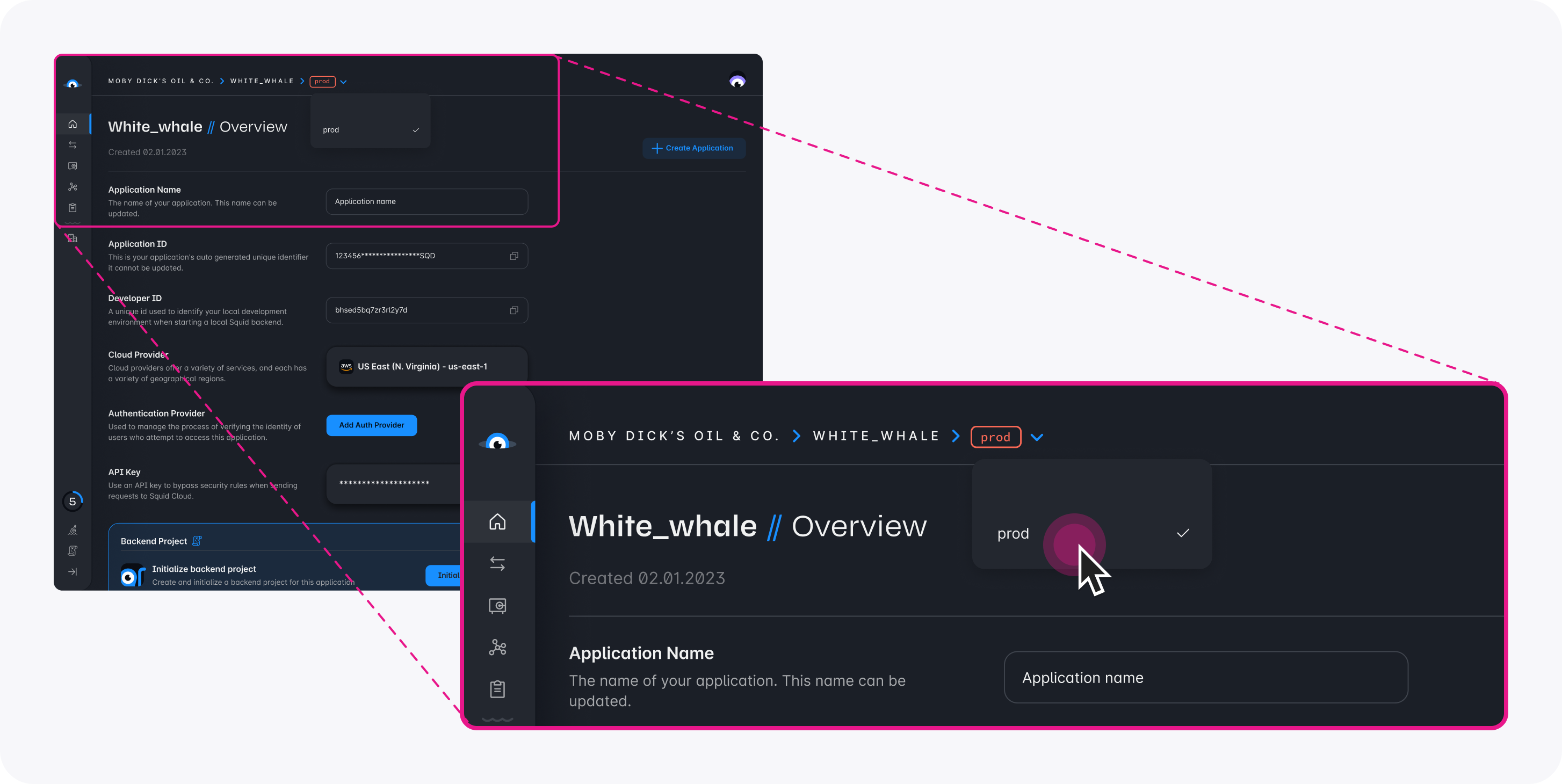
Download the ai-tutorial-squid-facts code sample using the following command. Replace the placeholders with the values from your Squid application as shown in the console.
npx @squidcloud/cli init-sample ai-tutorial-squid-facts --template ai-tutorial-squid-facts --appId YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID --apiKey YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY --environmentId dev --squidDeveloperId YOUR_SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID --region YOUR_REGION
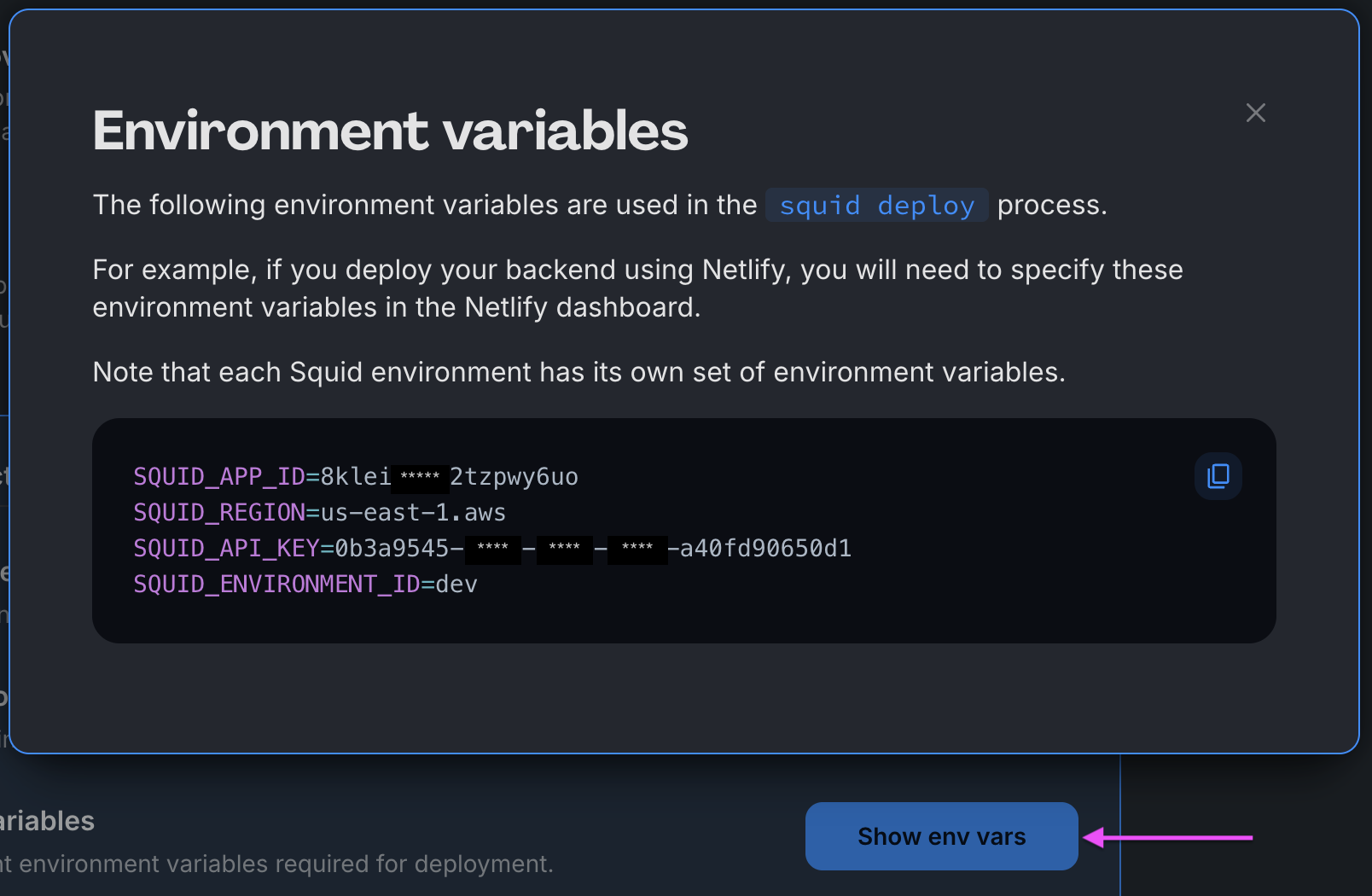
You can find your environment variables under: 'Application' -> 'Show env vars' as seen below:
- Open the project in the IDE of your choice.
- Start the app locally by running the following command in the project folder:
npm run start
- To view the app, navigate to localhost:PORT, where PORT is logged in the terminal. The address will likely be
http://localhost:5173.
Add the Squid AI Agent
-
In the Squid Console, select the Agent Studio tab.
-
Click Create New Agent to add an agent. Provide the following details, then click Create:
- Agent ID:
squid-facts - Description:
This is an agent for Squid AI's fact sharing tutorial
- On the Overview page of the AI agent, there are three sections: LLM Model, Instructions, and Abilities.
-
LLM Model: This is the underlying AI model that powers the agent. You can use the default GPT-4o model, or select a different one.
-
Instructions: This is the rule set for how the AI agent responds and answers questions. It can be about tone or purpose. Edit the squid-facts agent instructions to the following:
You're a friendly AI who shares random facts about squids and answers user questions about squids.
Important: Only answer based on the provided context. -
Abilities: This is the information and tools the agent uses when responding to questions. Learn more about abilities by reading the documentation.
To add squid facts to the agent's knowledge base, navigate to the Wikipedia article on squids and save the page as an HTML or PDF file. Next, in the console click Add Abilities. Select the File ability under Knowledge Base and upload the file. This ability allows the agent to use context when answering questions.
LLM models likely already know this squid information. In your own applications, you will provide context that is relevant to your use case.
-
Navigate to the Agent Settings tab of the AI agent, and scroll down to Set Agent to Public. Toggle this setting on so that the agent can be accessed by anyone on the frontend. See the documentation on securing your AI agent for more information.
-
Click the + next to Context to add context. Name the context Squid Wikipedia. Change the Context type to URL, and then enter the following URL:
Now that you have a Squid project with an AI agent, you're ready to add functionality to an app!
Configure the frontend
The following steps add configuration parameters to connect the application to Squid.
- Open a new terminal window and navigate to the project's frontend. You should now have two open terminal windows: one for the app's backend and one for the frontend.
cd frontend
- Install the required dependencies:
npm install
- Run the following command to create a
.env.localfile with the Squid environment configuration needed to initialize Squid:
npm run setup-env
Customize the frontend
- In the frontend, open the
squid-facts-ai.tsxcomponent, which is located in thecomponentsfolder. The folder holds a component that's pretty empty right now:
function SquidFactsAI() {
return <></>;
}
export default SquidFactsAI;
- Add the following import statement at the top of the file to use the AI agent on the frontend:
import { useAiChat } from '@squidcloud/react';
- In the
SquidFactsAI()function, add the following constants. They will be used to manage the state of the conversation with the AI agent:
const [question, setQuestion] = useState('');
const { history, chat, complete } = useAiChat('squid-facts');
The variables question and setQuestion use a standard useState hook to manage the state of a question the user asks.
The useAiChat hook wraps the AI agent. It takes the Agent ID as the second parameter, and returns several results, including chat, data, and complete.
To read more about useAiChat, check out the React SDK documentation.
- Add the following functions after the constants:
function askQuestion() {
chat(question);
setQuestion('');
}
function questionChanged(e: ChangeEvent) {
setQuestion((e.target as HTMLInputElement).value);
}
function checkKey(ele: React.KeyboardEvent<HTMLDivElement>) {
if (ele.key === 'Enter') {
askQuestion();
}
}
The askQuestion function calls the Squid Client SDK's chat function, which accepts a prompt for the AI agent in the form of a string.
The questionChanged and checkKey functions handle UI changes as the user asks a question.
- Replace the existing return with the following code:
return (
<>
<div className="scrolling">
<Messages messages={history} />
</div>
<div className="question">
<TextField fullWidth id="outlined-basic" label="Enter your question" variant="outlined" onChange={questionChanged} onKeyDown={(event) => checkKey(event)} value={question} />
<Button variant="contained" disabled={!complete} onClick={askQuestion}>
Ask question
</Button>
</div>
</>
);
This code passes the chat history to the Messages component, which displays the conversation between the user and the AI agent. It also includes an input component where the user asks questions, and a button to trigger the askQuestion function.
- Add the relevant imports for things we've added. The imports should look like this:
import { useAiChat } from '@squidcloud/react';
import Messages from './messages.tsx';
import { Button, TextField } from '@mui/material';
import React, { ChangeEvent, useState } from 'react';
- Open the
messages.tsxfile. Replace all of the contents of the file with the following code. This code iterates through the array of chat messages and displays them:
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { ChatMessage } from '@squidcloud/react';
interface ChatHistoryProps {
messages: ChatMessage[];
}
const Messages: React.FC<ChatHistoryProps> = ({ messages }) => {
const messagesEndRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const scrollToBottom = () => {
messagesEndRef.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};
useEffect(() => {
scrollToBottom();
}, [messages]);
return (
<div>
{messages.map(({ id, message, type }) => (
<div key={id}>
<span key={id}>
{type}: {message}
</span>
</div>
))}
<div ref={messagesEndRef} />
</div>
);
};
export default Messages;
Run the code
- In the root project folder, run the following command to view the app:
npm run start
To view the app, navigate to localhost:PORT where PORT is logged in the terminal. The address will likely be http://localhost:5173.
Why is there a picture of a squid on the page, you ask? Of course you don't ask. It's an app about squids.
- Ask the AI agent some questions about squids. Here are some examples if you're stumped:
- Do squids have arms or tentacles?
- What should I do if I encounter a squid?
- What's your favorite fact about squids?
- Tell me about the Onykia ingens.
Share your favorite squid questions and answers with the Squid Squad on Discord or X.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You just created a Squid AI application. Feel free to keep asking questions to see just how much this AI agent knows about squids!
Next steps
Now that you know how to create public Squid AI agents, here are some next steps you can take:
-
Add a new agent based on your use case. For example, Squid AI can support a different persona for each part of your user engagement: sales, support, product experts and more.
-
Implement a Squid security rule that limits access to the Squid AI.
-
Connect your database to your frontend using Squid middle tier to enable data access capabilities through the Squid Client SDK.