Add security to a Squid AI Agent
Secure a Squid AI agent using Auth0 authentication and backend authorization.
With Squid AI, you can create rich AI agent experiences built on unique context and tools that you provide. You can secure your AI agents in just a few lines of code using Squid's robust backend functionality.
Rules can be as basic or as customized as you need to fit your unique use case. By using the @secureAiAgent decorator, you can turn a TypeScript function into an endlessly customizable AI agent security solution. And since security functions are written in TypeScript, writing, interpreting, and updating security rules is as straightforward as updating any other function.
This tutorial goes thoroughly into the "what" and "why" of the steps to take to create and secure an AI agent so that by the end, you can feel confident in your understanding of Squid AI Agents.
What you'll build
- A custom AI agent configured with authentication and authorization to limit chat access
- A React frontend application in which to run the Squid AI Agent
What you'll learn
- How to create a Squid AI agent
- How to provide context to your AI agent
- How to incorporate your Squid AI agent into a frontend
- How to create a Squid Service that adds security to your AI agent
What you'll need
- The Squid CLI
- An account in the Squid Console
- An Auth0 account with a single-page application configured to use React
Environment setup
- In the Squid Console, switch to the
devenvironment.
Download the ai-tutorial-secure-chat code sample using the following command. Replace the placeholders with the values from your Squid application as shown in the console.
npx @squidcloud/cli init-sample ai-tutorial-secure-chat --template ai-tutorial-secure-chat --appId YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID --apiKey YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY --environmentId dev --squidDeveloperId YOUR_SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID --region YOUR_REGION
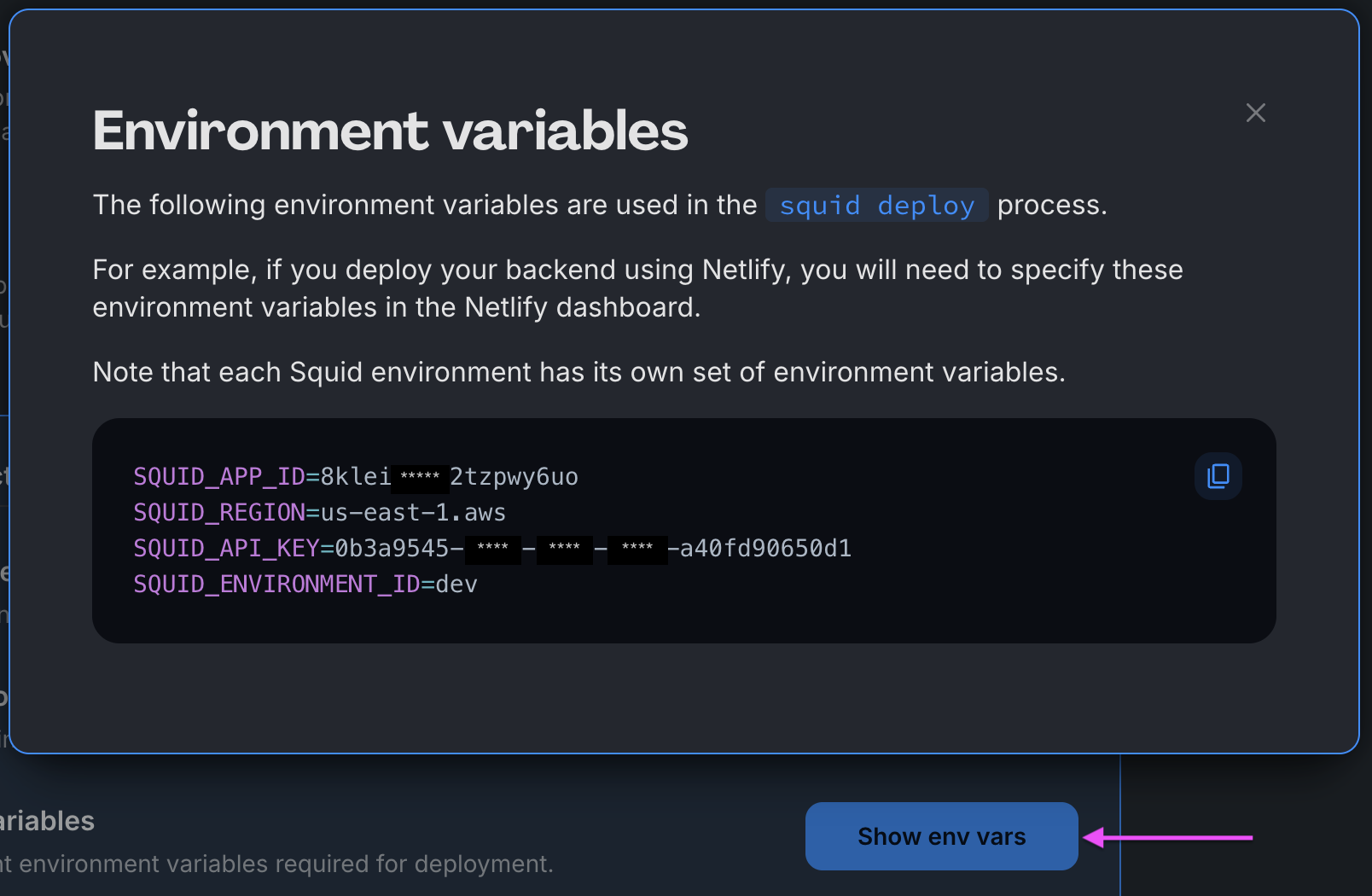
You can find your environment variables under: 'Application' -> 'Show env vars' as seen below:
- Open the project in the IDE of your choice.
- Start the app locally by running the following command in the project folder:
npm run start
- To view the app, navigate to localhost:PORT, where PORT is logged in the terminal. The address will likely be
http://localhost:5173.
Add the Squid AI Agent
- Select the Agent Studio tab in the Squid Console
- Click Create New Agent to add an agent. Provide the following details, then click Create:
- Agent ID:
squid-facts-chatbot - Description:
This is an agent for Squid AI's secure chat tutorial.
- On the Overview page of the AI agent, navigate to the Instructions section. Add the following instructions:
You're a friendly AI who shares random facts about squids and answers user questions about squids.
Important: Only answer based on the provided context.
- To add squid facts to the agent's knowledge base, navigate to the Wikipedia article on squids and save the page as an HTML or PDF file. Next, in the Agent Overview page click Add Abilities. Select the File ability under Knowledge Base and upload the file. This ability allows the agent to use context when answering questions.
LLM models likely already know this squid information. In your own applications, you will provide context that is relevant to your use case.
Add the Auth0 connector
-
If you haven't yet made an Auth0 application, first set up an Auth0 account.
Next, navigate to the Auth0 Dashboard and create a single-page application configured to use React. Be sure to add
http://localhost:5173in the application's settings for Allowed Callback URLs, Allowed Logout URLs, and Allowed Web Origins.Finally, create an Auth0 API (located under the Applications sidebar item) using
squid-aias the API audience. -
In the Squid Console in the
devenvironment, select the Connectors tab . -
Click the Available connectors tab and add an Auth0 connector
- Connector ID:
auth0 - Auth0 Domain: This value can be found in the your Auth0 application's settings
- Audience:
squid-ai, or the value you input when creating the Auth0 API
- Click Add connector.
Add Auth0 credentials
- Navigate to
squid-facts/frontend/src/main.tsx. Notice there is anAuth0Providercomponent, that requires configuration. Replace the placeholders in theAuth0Providercomponent with the domain and client ID from your Auth0 application:
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root') as HTMLElement).render(
<Auth0Provider
domain="AUTH0_DOMAIN"
clientId="AUTH0_CLIENT_ID"
authorizationParams={{
redirect_uri: window.location.origin,
audience: 'squid-ai',
}}
>
<SquidContextProvider
options={{
appId: import.meta.env.VITE_SQUID_APP_ID,
region: import.meta.env.VITE_SQUID_REGION,
environmentId: import.meta.env.VITE_SQUID_ENVIRONMENT_ID,
squidDeveloperId: import.meta.env.VITE_SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID,
}}
>
<App />
</SquidContextProvider>
</Auth0Provider>
);
- Open the
App.tsxfile and add the following imports:
import { useAuth0 } from '@auth0/auth0-react';
import { useSquid } from '@squidcloud/react';
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
This imports the Auth0 and Squid React libraries, along with some standard React functionality.
- Add the following code to the
Appfunction:
// Get Auth0 authentication state.
const { user, isLoading, getAccessTokenSilently } = useAuth0();
const { setAuthProvider } = useSquid();
useEffect(() => {
setAuthProvider({
integrationId: 'auth0',
getToken: () => user && getAccessTokenSilently(),
});
if (isLoading) return;
if (!user) {
setLoginMessage('You are logged out!');
setToastOpen(true);
} else {
setLoginMessage('You are logged in!');
setToastOpen(true);
}
}, [user, isLoading, getAccessTokenSilently, setAuthProvider]);
if (isLoading) {
return <span>Loading...</span>;
}
This code sets the auth provider in your Squid application, passing the Access token from Auth0 to the Squid backend.
- In the return statement, change the value of the
isAuthenticatedprop fromfalseto!!user:
<NavBar isAuthenticated={!!user} />
This informs the NavBar of which button to display: a login button or a logout button.
Checkpoint
At this point, you have added all the code that will be in App.tsx. Here's a look at the final file:
import SquidFactsAI from './components/squid-facts-ai';
import './App.css';
import NavBar from './components/nav-bar';
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { useAuth0 } from '@auth0/auth0-react';
import { useSquid } from '@squidcloud/react';
import { Snackbar, Alert } from '@mui/material';
function App() {
// Set state of toast message
const [toastOpen, setToastOpen] = useState(false);
const [loginMessage, setLoginMessage] = useState('');
// Get Auth0 authentication state
const { user, isLoading, getAccessTokenSilently } = useAuth0();
const { setAuthProvider } = useSquid();
useEffect(() => {
setAuthProvider({
integrationId: 'auth0',
getToken: () => user && getAccessTokenSilently(),
});
if (isLoading) return;
if (!user) {
setLoginMessage('You are logged out!');
setToastOpen(true);
} else {
setLoginMessage('You are logged in!');
setToastOpen(true);
}
}, [user, isLoading, getAccessTokenSilently, setAuthProvider]);
if (isLoading) {
return <span>Loading...</span>;
}
const handleToClose = () => {
setToastOpen(false);
};
return (
<>
<NavBar isAuthenticated={!!user} />
<img src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e1/Sepioteuthis_sepioidea_%28Caribbean_Reef_Squid%29.jpg" />
<SquidFactsAI />
<Snackbar open={toastOpen} onClose={handleToClose} autoHideDuration={6000}>
<Alert severity="success">{loginMessage}</Alert>
</Snackbar>
</>
);
}
export default App;
Add Squid AI Agent functionality
- In the
src/componentsfolder, open thesquid-facts-ai.tsxfile. Scroll down to the return statement and notice that there is aTextFieldcomponent and aButtoncomponent. This is where the user asks questions to the AI agent. There is also an emptydivcomponent where the chat history will be displayed. Add the following imports:
import Messages from './messages';
import { useAiChat } from '@squidcloud/react';
The useAiChat function lets the client use Squid AI to chat.
- Add the following to the
SquidFactsAIfunction:
const { history, chat, complete, error } = useAiChat('squid-facts-chatbot');
- Right now the
askQuestionfunction just sets the value ofquestionto an empty string, but it doesn't actually ask the question. Add thechatfunction toaskQuestionto ask questions to the AI agent:
function askQuestion() {
chat(question);
setQuestion('');
}
- Add the
Messagescomponent to the emptydiv:
<div className="scrolling">
<Messages messages={history} />
</div>
This passes the conversation history to a prop in the Messages component, which then displays it.
- Update the
Buttonso that it is disabled until a chat response is complete, and then add adivthat displays the error message if an error occurs when using the AI agent:
...
return (
...
<Button variant="contained" disabled={!complete} onClick={askQuestion}>
Ask question
</Button>
{ error && <div>{error.toString()}</div>}
...
)
Checkpoint
You have now completed the code for this component. Here is all the code for the squid-facts-ai.tsx file:
import { ChangeEvent, useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button } from '@mui/material';
import Messages from './messages';
import { useAiChat } from '@squidcloud/react';
const SquidFactsAI = () => {
const [question, setQuestion] = useState('');
const { history, chat, complete, error } = useAiChat('squid-facts-chatbot');
function askQuestion() {
chat(question);
setQuestion('');
}
function questionChanged(e: ChangeEvent) {
setQuestion((e.target as HTMLInputElement).value);
}
function checkKey(ele: React.KeyboardEvent<HTMLDivElement>) {
if (ele.key === 'Enter') {
askQuestion();
}
}
return (
<>
<div className="scrolling">
<Messages messages={history} />
</div>
<div className="question">
<TextField fullWidth id="outlined-basic" label="Enter your question" variant="outlined" onChange={questionChanged} onKeyDown={(event) => checkKey(event)} value={question} />
<Button variant="contained" disabled={!complete} onClick={askQuestion}>
Ask question
</Button>
{error && <div>{error.toString()}</div>}
</div>
</>
);
};
export default SquidFactsAI;
Set up the Messages component
Open the messages.tsx file and replace the contents of the file with the following code:
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { ChatMessage } from '@squidcloud/react';
interface ChatHistoryProps {
messages: ChatMessage[];
}
const Messages: React.FC<ChatHistoryProps> = ({ messages }) => {
const messagesEndRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const scrollToBottom = () => {
messagesEndRef.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
};
useEffect(() => {
scrollToBottom();
}, [messages]);
return (
<div className="messages">
{messages.map(({ id, message, type }) => (
<div key={id}>
<span key={id}>
<b>{type}:</b> {message}
</span>
</div>
))}
<div ref={messagesEndRef} />
</div>
);
};
export default Messages;
This code displays the chat messages. The type of a ChatMessage is the author of the message. It is either the user or AI.
Secure the AI agent on the Squid backend
Navigate to the backend folder. This contains any Squid backend logic. Open the src/service/ai-security-service.ts file. Add the following code to the file:
import { secureAiAgent, SquidService } from '@squidcloud/backend';
export class AiSecurityService extends SquidService {
@secureAiAgent('squid-facts-chatbot')
allowChat(): boolean {
// or add custom authorization here
return this.isAuthenticated();
}
}
This creates a Squid Service that allows the client to chat with the AI agent if they are authenticated. The setAuthProvider function we called on the frontend informed the backend of the user's authentication status. The @secureAiAgent decorator is used to set security rules. While this example only verifies that the user is authenticated, you can add customized authorization rules. For example, you could query a database to check if the user is part of a permitted list of users.
Check out the documentation to learn more about security and authentication.
Try out the app
- To run the backend locally, run the following command in the
backenddirectory:
squid start
- In a separate terminal window, run the following command from the
frontenddirectory:
npm run dev
You now have two terminal windows: one running the backend and the other running the frontend.
-
To view the app, navigate to localhost:PORT where PORT is logged in the terminal. The address will likely be
http://localhost:5173. -
Ask a question about squids to the AI agent. Notice you do not get a response. Instead, an unauthorized message appears.
-
Log into the app and ask a question again. Now the AI agent will chat with you!
Feel free to keep asking questions and to see what happens when you log out and in. With the Squid Service on the backend handling authorization, you can rest easy knowing only authenticated users will have access to the service.
Here are some questions to try:
- Do squids have arms or tentacles?
- What should I do if I encounter a squid?
- What's your favorite fact about squids?
- Tell me about the Onykia ingens.
Share your favorite squid questions and answers with the Squid Squad on Discord or X.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You just added a customized AI agent to an app, and then secured it using the Squid Backend SDK. Feel free to keep asking questions to see just how much this AI agent knows about squids!
Next steps
Now that you know how to limit AI agent access to authenticated users, here are some other things to try:
- Add a new AI agent based on your use case. For example, Squid AI agents can support a different persona for each part of your user engagement: sales, support, product experts and more.
- Connect your database to your frontend using Squid middle tier to enable data access capabilities through the Squid Client SDK.
- Think of other properties on which you might secure your Squid AI Agent. For example, you might want users to sign a consent form first. You can log consent status in your database, and then verify on the backend that the user is logged in and has signed the consent form.
Clean up
To prevent further billing, delete the Squid app in the Squid Console by selecting the Overview tab for the app and scrolling down to Delete Application.