Connect an AI agent to a database
Connect APIs to Squid to build an agent that writes to the database to create a packing list
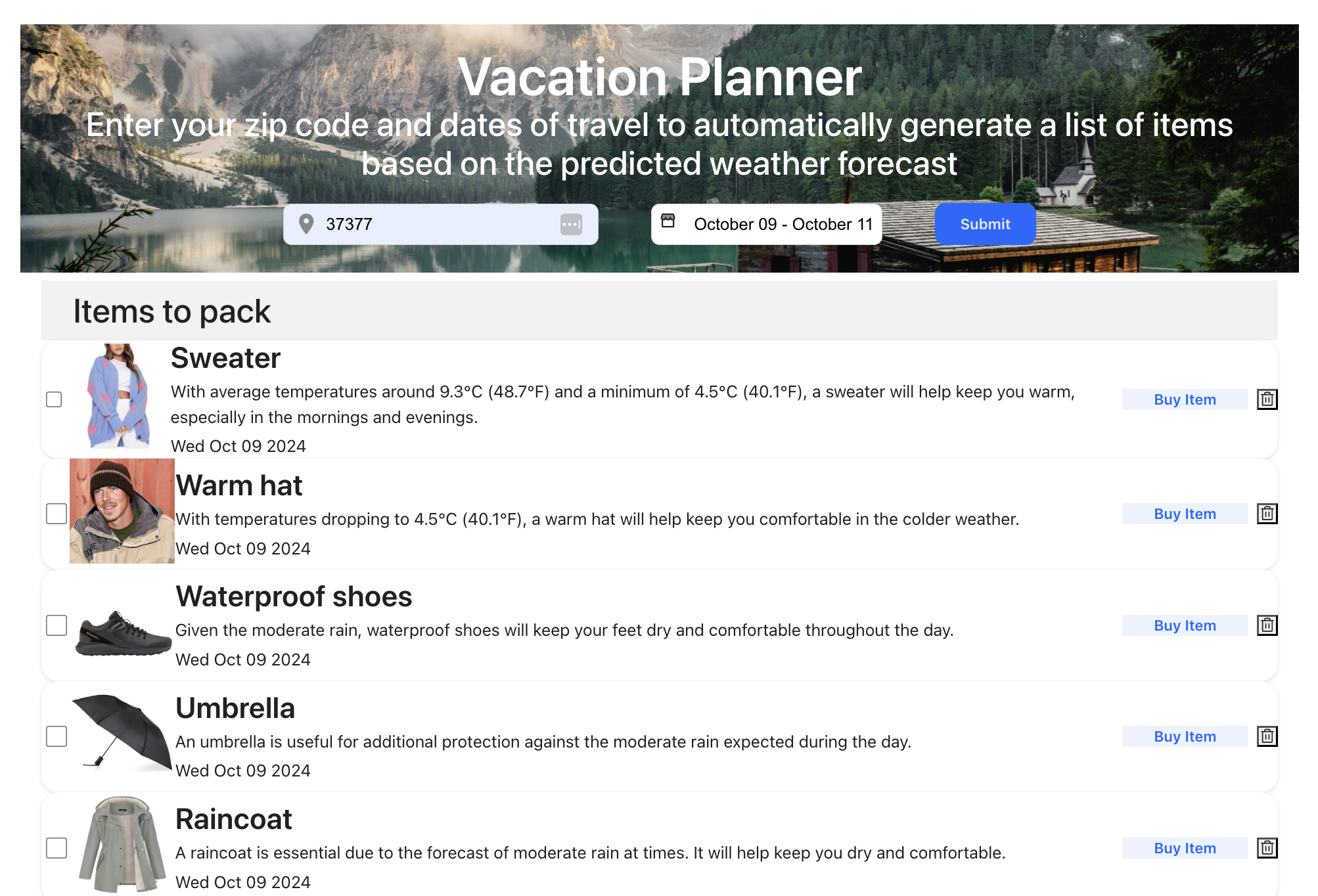
What you'll build
- A fullstack app that creates a list of items to pack for a vacation based on the zip code and travel dates you provide.
- The app checks the predicted weather using an external API, creates a list of items to pack based on the weather, and writes these items to your database.
This application integrates with WeatherAPI.com to get the forecast for a given location and date, and then passes the information to an AI agent that uses an AI function to write suggested packing items to Squid's built-in database
This functionality is extended using a Real-time Product Search API to provide links to suggested items to purchase from Google Shopping, showcasing how simple it is to integrate multiple services with AI functionality using Squid.
What you'll learn
- How to create an AI agent using Squid AI.
- How to add functions to an agent.
You'll need some experience with TypeScript. Experience with React is useful, but not required.
Environment setup
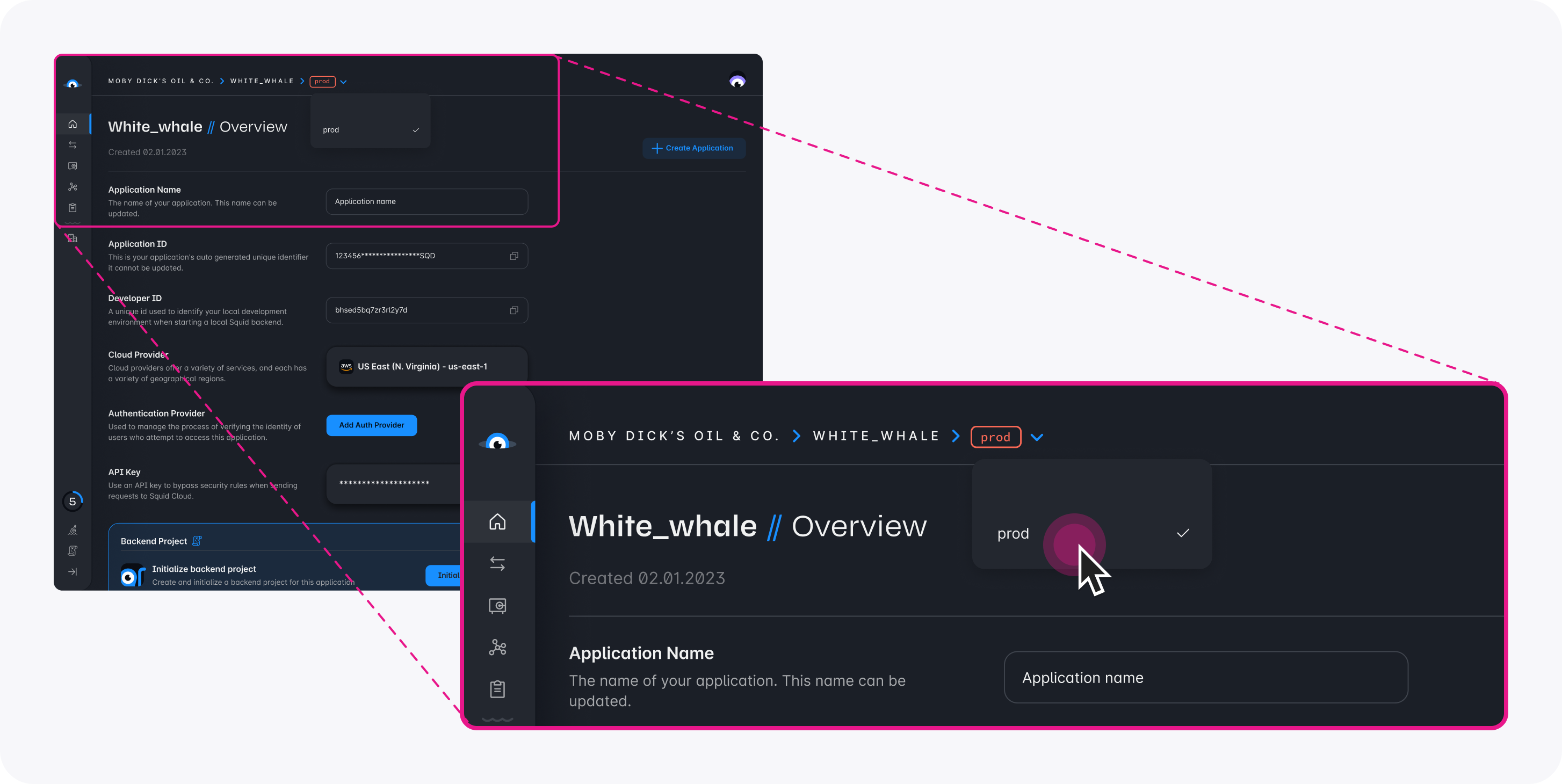
- In the Squid Console, switch to the
devenvironment.
Download the squid-ai-vacation code sample using the following command. Replace the placeholders with the values from your Squid application as shown in the console.
npx @squidcloud/cli init-sample squid-ai-vacation --template
squid-ai-vacation --appId YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID --apiKey
YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY --environmentId dev --squidDeveloperId
YOUR_SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID --region YOUR_REGION
- Open the project in the IDE of your choice.
- Start the app locally by runnning the following command in the project folder:
npm run start
- To view the app, navigate to localhost:PORT where PORT is logged in the terminal. The address will likely be
http://localhost:5173.
Create a WeatherAPI.com account
To get weather forecasts, this application uses an API available from WeatherAPI.com. The API offers a free trial so you can use it in this sample at no charge.
-
Sign up for WeatherAPI.com's free trial.
-
In the WeatherAPI.com dashboard, you can find your WeatherAPI.com API key. Take note of this key because you will need it for the API connector.
Connecting WeatherAPI.com
To connect an API with Squid, you will most often add an HTTP API connector in the Squid Console, but it is not required for this tutorial. To learn more, check out the documentation on HTTP API connectors.
- For this application, you can generate the API connector using cURL commands. In a terminal window, run the following command, changing the placeholders for
YOUR_SQUID_APP_IDandYOUR_SQUID_API_KEYto the values from your Squid app. You can find the correct values in the Backend Project section of the application overview page of the Squid Console or in your.envfile.
curl -X PUT https://console.us-east-1.aws.squid.cloud/openapi/iac/applications/YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID-dev/integrations/weather -H "x-app-api-key: YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"id": "weather",
"configuration": {
"discoveryOptions": {}
},
"type": "api"
}'
- Run the following cURL command to populate the API schema, changing the placeholders for
YOUR_SQUID_APP_IDandYOUR_SQUID_API_KEYto the values from your Squid app.
curl -X PUT https://console.us-east-1.aws.squid.cloud/openapi/iac/applications/YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID-dev/integrations/weather/schema -H "x-app-api-key: YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"type": "api",
"baseUrl": "https://api.weatherapi.com/v1",
"endpoints": {
"realtime-weather": {
"relativePath": "/current.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"lang": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"forecast-weather": {
"relativePath": "/forecast.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"days": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"unixdt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"hour": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"lang": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"alerts": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"aqi": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"tp": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"future-weather": {
"relativePath": "/future.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"lang": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {
"location": {
"location": "body",
"path": "location",
"description": null
},
"forecast": {
"location": "body",
"path": "forecast",
"description": null
}
},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"history-weather": {
"relativePath": "/history.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"unixdt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"end_dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"unixend_dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"hour": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"lang": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"marine-weather": {
"relativePath": "/marine.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"days": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"unixdt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"hour": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"lang": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"search-autocomplete-weather": {
"relativePath": "/search.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"ip-lookup": {
"relativePath": "/ip.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"time-zone": {
"relativePath": "/timezone.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": null,
"tags": null
},
"astronomy": {
"relativePath": "/astronomy.json",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"dt": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {},
"injectionSchema": {},
"tags": null
}
},
"injectionSchema": null
}'
View and update the Weather API schema
WeatherAPI.com requests require an API key. With Squid, you can securely store your API key using Squid Secrets. You can even automatically include the key with all requests using Squid's injection feature.
- In the Squid Console, navigate to your weather connector schema.
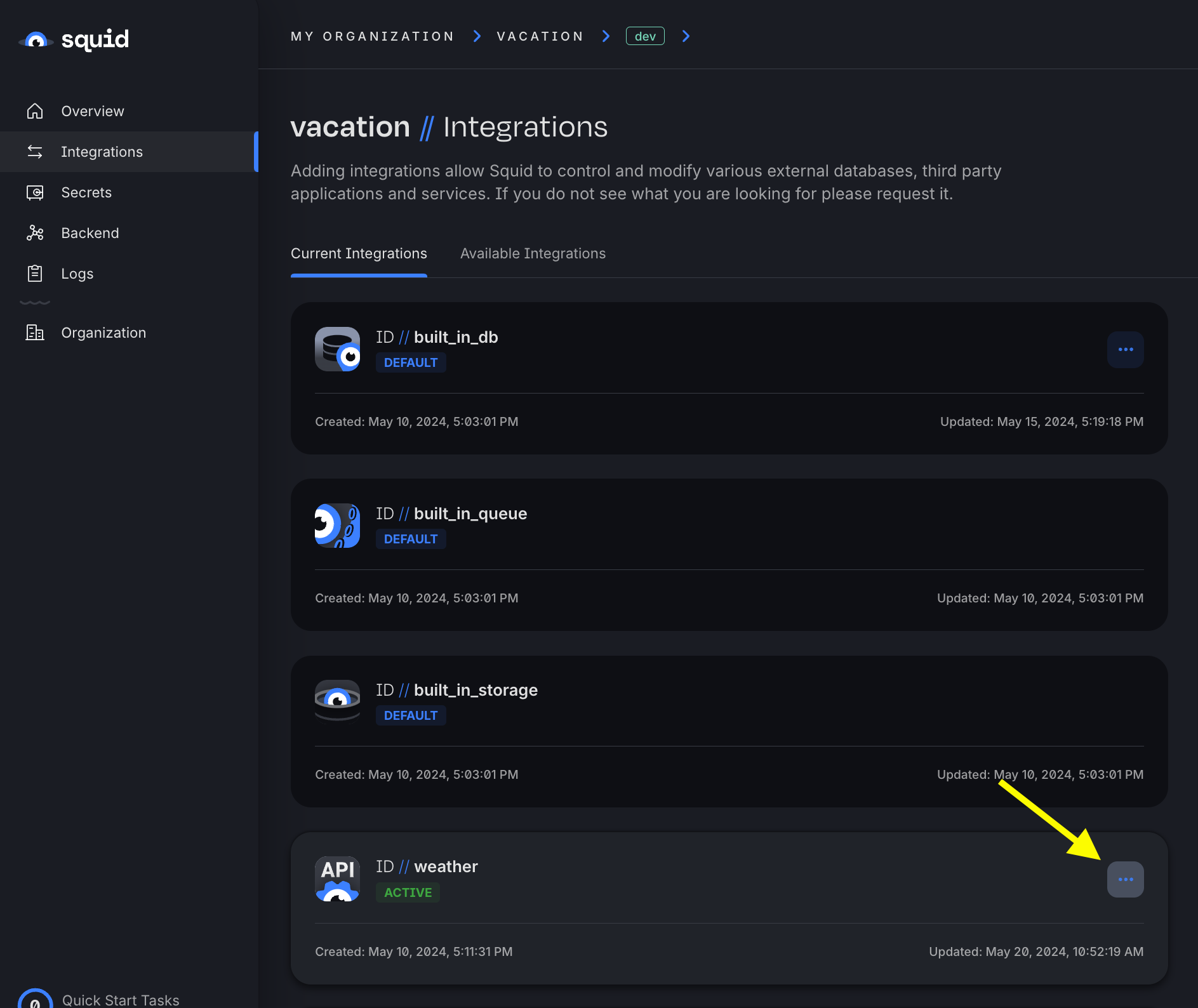
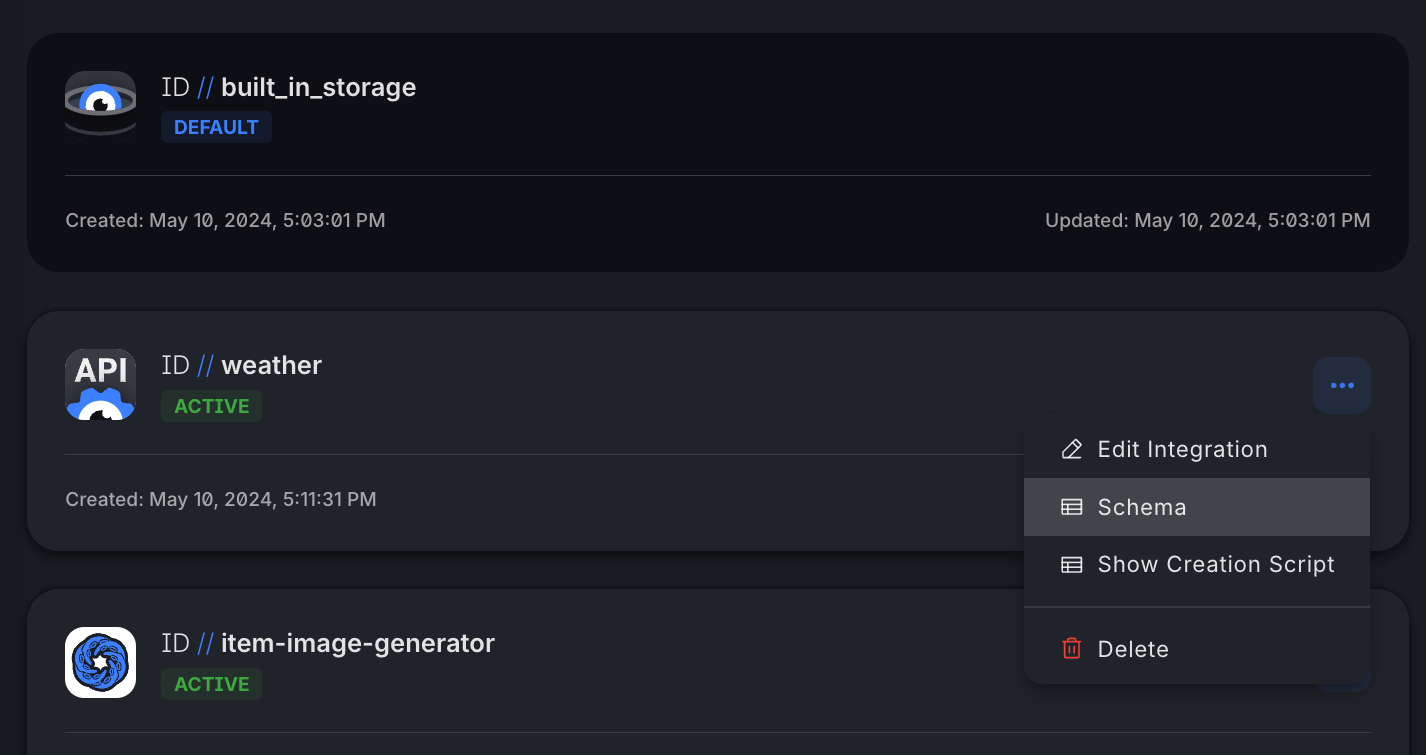
- Click on the base URL, which is
https://api.weatherapi.com/v1.
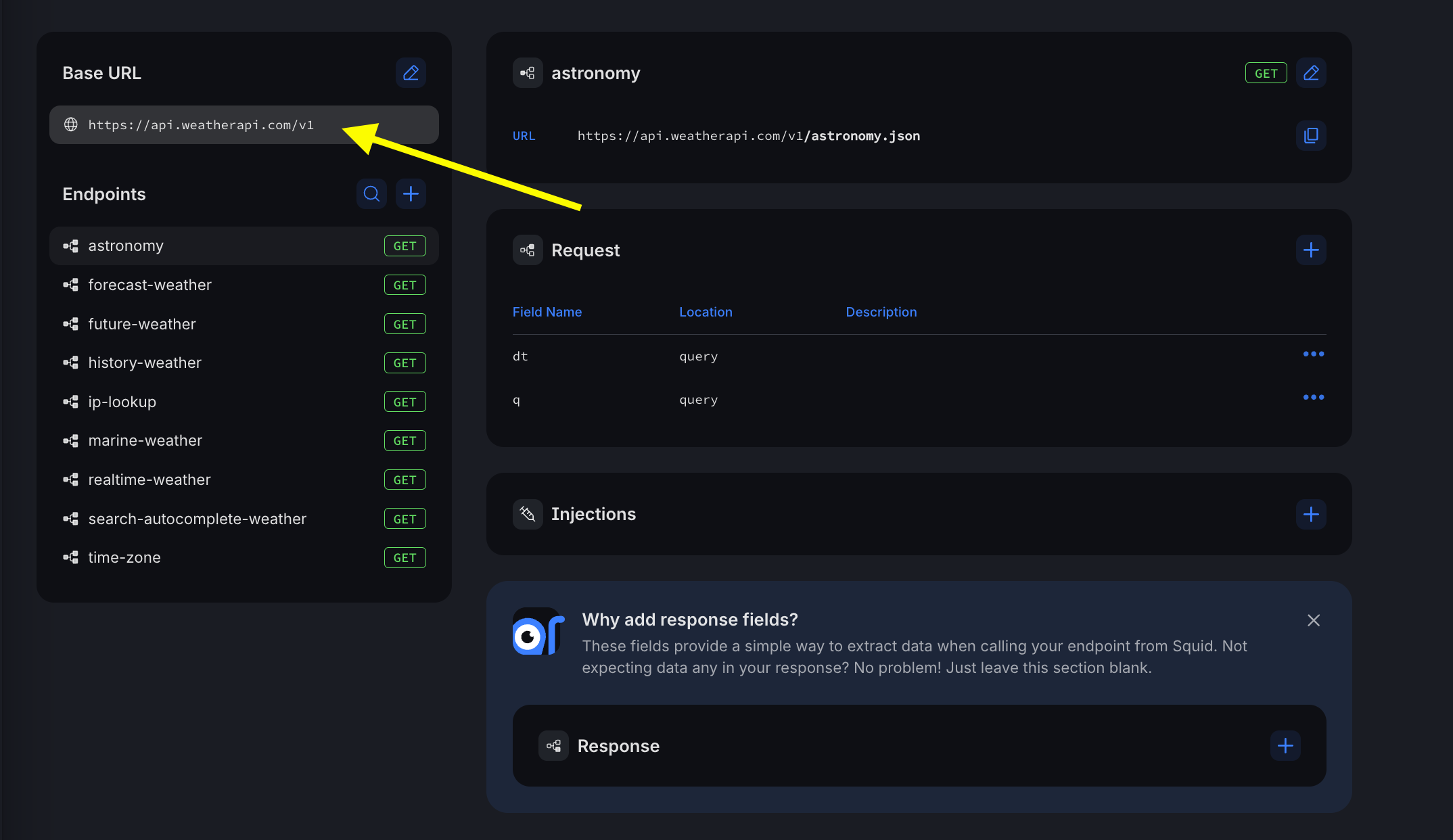
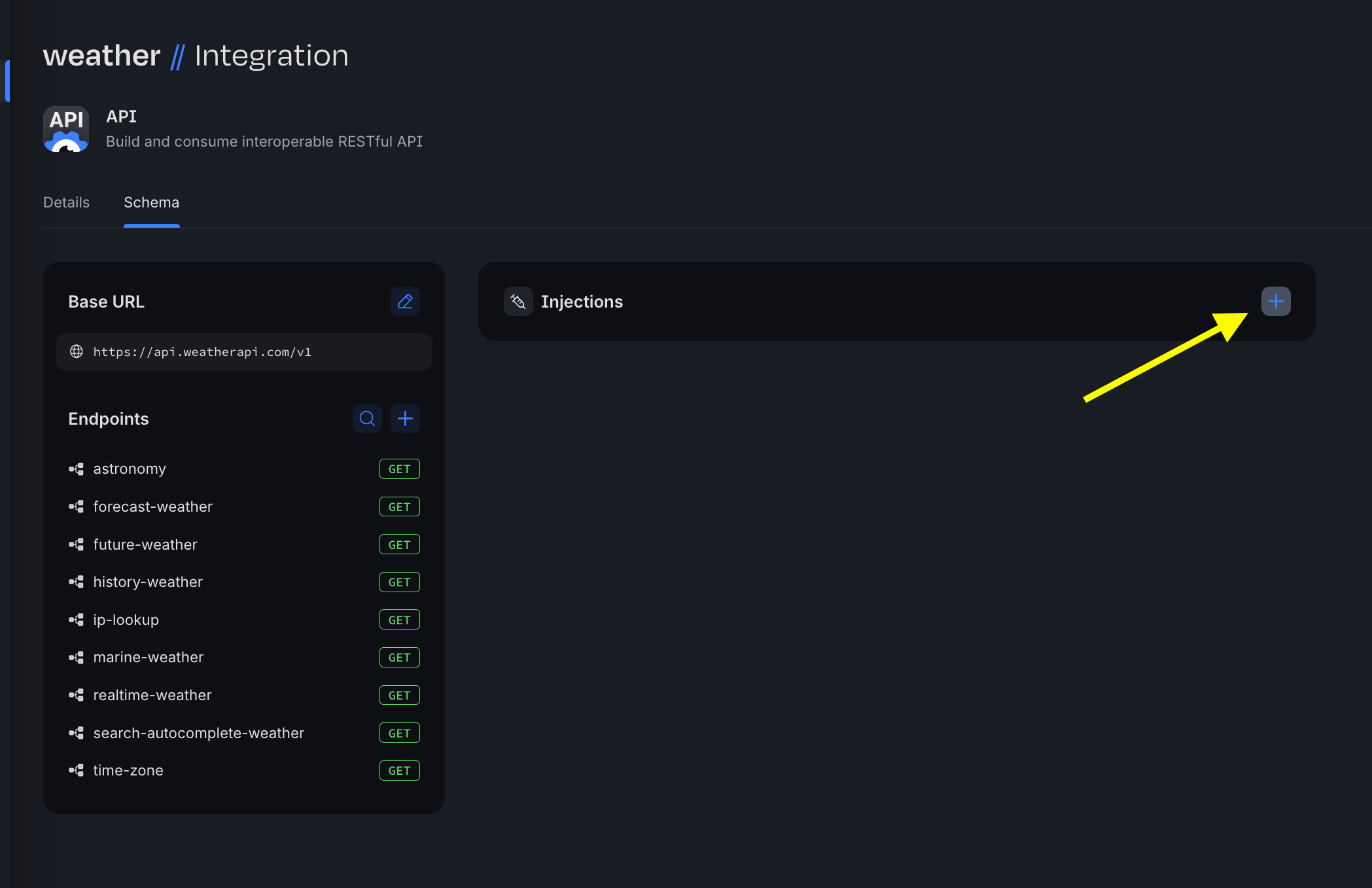
- Click the + in the Injections area to add a new injection.
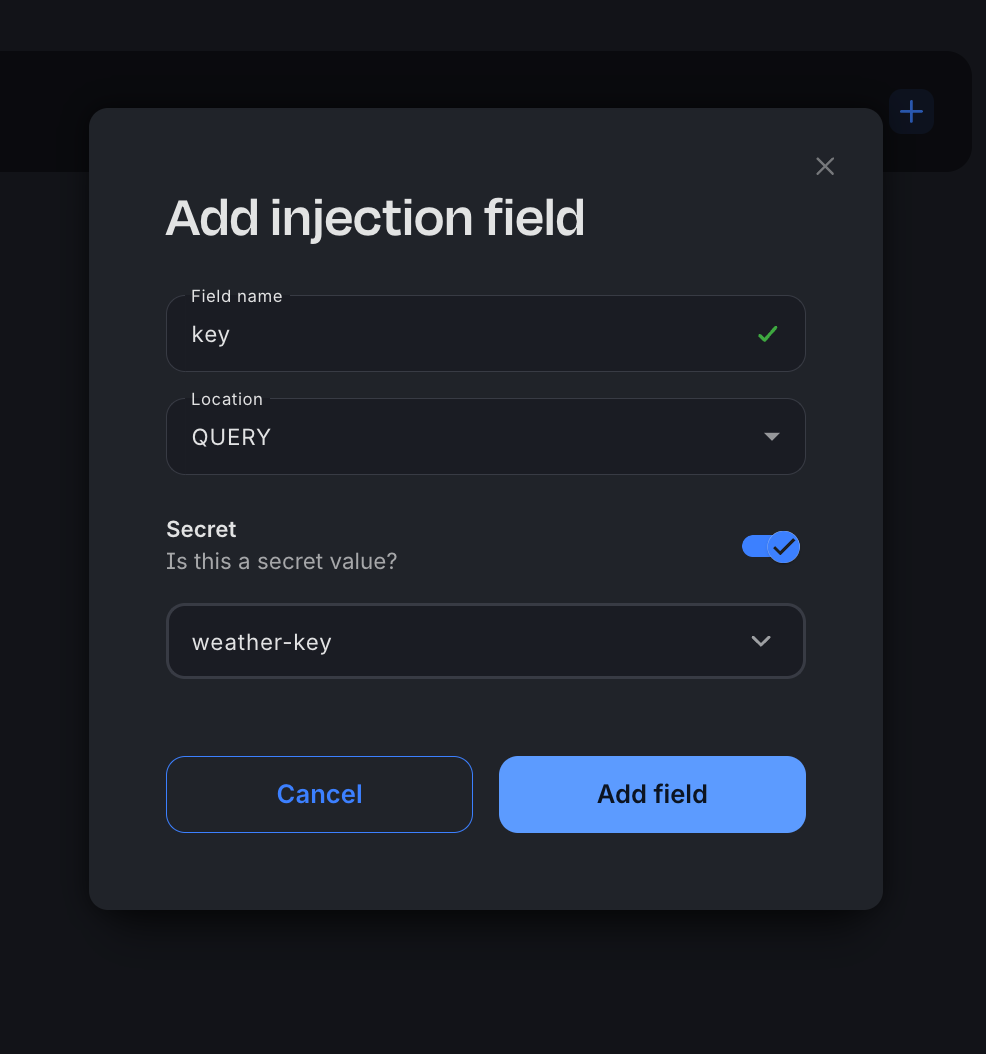
- The Field name is key and the Location is query. Toggle Secret on, and then create a new secret. For the secret value, paste in your WeatherAPI.com API key. Ensure that the secret is saved and selected, and then save the new injection.
Connect to the Real-time Product Search API
In case you don't own an item that was suggested by the AI agent, the app provides links to Google Shopping so you can easily purchase what you need. This is achieved using a product search API available on RapidAPI.
- Navigate to the Real-time Product Search API, and subscribe. Like the WeatherAPI.com API, you will need your API key. Once you sign up, your API key is visible on the API's landing page.
- Generate your Squid connector using the following command, changing the placeholders for
YOUR_SQUID_APP_IDandYOUR_SQUID_API_KEYto the values from your Squid app:
curl -X PUT https://console.us-east-1.aws.squid.cloud/openapi/iac/applications/YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID-dev/integrations/product-search -H "x-app-api-key: YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"id": "product-search",
"configuration": {
"discoveryOptions": {}
},
"type": "api"
}'
- Add the API schema to the connector by running the following cURL command, changing the placeholders for
YOUR_SQUID_APP_IDandYOUR_SQUID_API_KEYto the values from your Squid app:
curl -X PUT https://console.us-east-1.aws.squid.cloud/openapi/iac/applications/YOUR_SQUID_APP_ID-dev/integrations/product-search/schema -H "x-app-api-key: YOUR_SQUID_API_KEY" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"type": "api",
"baseUrl": "https://real-time-product-search.p.rapidapi.com",
"endpoints": {
"search": {
"relativePath": "search",
"method": "get",
"requestSchema": {
"q": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"country": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"language": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"limit": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
},
"sort_by": {
"location": "query",
"description": null
}
},
"responseSchema": {
"data": {
"location": "body",
"path": "data",
"description": null
}
},
"injectionSchema": {
"X-RapidAPI-Host": {
"value": "real-time-product-search.p.rapidapi.com",
"type": "regular",
"location": "header"
}
},
"tags": null
}
},
"injectionSchema": null
}'
-
In the Squid Console, click the Connectors tab navigate to your product-search connector schema, just like you did with the weather connector.
-
Click on the search endpoint.
-
Click the + in the Injections area to add a new injection.
-
The Field name is X-RapidAPI-Key and the Location is header. Toggle Secret on, and then create a new secret. For the secret value, paste in your RapidAPI API key. Ensure that the secret is saved and selected, and then save the new injection.
Add the AI Agent
-
In the Squid Console, navigate to the Agent Studio tab.
-
Click Create New Agent to add an agent. Provide the following details, and then click Add:
- Agent ID:
planner - Description:
This is an agent for Squid AI's vacation planner tutorial
-
Click Create to create the agent.
-
In the Instructions field, and add the following instructions to the agent:
You are designed to create a list of items to pack for a trip based on the provided weather forecast and date, where the date is a string. You should create 3-5 items.
These instructions tell the AI agent what actions to take.
Explore your Squid application
With both your frontend and your backend running, visit http://localhost:5173/ in your web browser. You're now ready to experiment with the count button and explore the functionalities of your Squid application:
-
Enter a zip code for a prospective vacation destination. For example, 90210.
-
Enter a start and end vacation date within the next 14-90 days. For demonstration purposes, this application limits you to a 5 day vacation. This helps limit the number of API calls the app makes.
-
Click Submit, and watch as your suggested packing items roll in!
Next steps
- To learn more about Squid AI agents, view the documentation.
- To learn more about Squid's real-time data capabilities, view the Client SDK documentation.
- To find out how to integrate with your own data sources, view the database connectors documentation.