Environments
Squid provides two environments for your work – dev and prod.
When you create a new application, Squid automatically sets up a dev and a prod environment. Use the dev environment for your development and testing. The prod environment is for when you're ready to take your application live.
Shared Between dev and prod | Not Shared Between dev and prod |
|---|---|
| App ID | Connectors |
| Region | Secrets |
| Organization | Built-in database |
| Developer ID | Backend deployments |
| API Keys |
Environments and connectors
When toggling between the dev and prod versions of your app in the Squid Console, you will notice that each has a different set of connectors.
To prevent unwanted changes to your production app's functionality, the connectors in your dev and prod environments are not synced. When adding a connector to your Squid app, confirm that you are adding it to the desired environment.
Connect your dev environment with development versions of your connectors. This allows you to build and test functionality without modifying the production version of your application.
If you choose the same connector ID for a given connector in both your dev and prod environments, you can develop in dev and then push to prod without having to change any variables in your code.
The dev environment
The dev environment is a complete backend application separate from your prod environment's application.
Running the dev backend locally
When initializing your Squid backend from the application overview page of the Squid Console, you are prompted to switch to dev mode.
The terminal command provided creates a new backend with a .env file. This file contains the attributes needed to run your backend locally, including a SQUID_ENVIRONMENT_ID. This value determines which environment your backend will run in.
Run the following command in your backend directory to run the backend locally:
squid start
To run your frontend with the locally running version of your backend, you must include your Squid Developer ID in your frontend Squid Client SDK configuration:
<SquidContextProvider
options={{
appId: 'YOUR_APP_ID',
region: 'YOUR_REGION', // example: 'us-east-1.aws'
environmentId: 'dev',
squidDeveloperId: 'YOUR_SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID',
}}
>
<App />
</SquidContextProvider>
Your Squid Developer ID is for local development only. Do not include your developer ID in your frontend app.
The prod environment
The production environment of your Squid application is the version your users should interact with. When adding connectors to the prod version of Squid, use the production version of your services.
Deploying your Squid backend
When you deploy your Squid backend, you must choose which environment to deploy it to.
Deploying to dev provides a staging environment where collaborators can test functionality. Once the dev backend is deployed, it is live and accessible from your app frontend without using the squidDeveloperId parameter in your Squid context.
Deploying to prod creates the live version of your backend that your users interact with. This overwrites any previous versions of your deployed backend.
To deploy a Squid backend to your dev environment, run the following command from your backend project's directory:
squid deploy
When ready to push a version of your backend to prod, use the following command:
squid deploy --environmentId prod --apiKey YOUR_PROD_API_KEY
You can find your prod deploy command and the prod API key in the Squid Console. Click the Deploy backend button in the Backend project section to find the command.
Selecting your environment
Environments in the console
Verify you are in the correct environment before adding or managing connectors in the console. To toggle between environments in the Squid Console, select the environment name at the top of the console, and then select the environment you want to display.
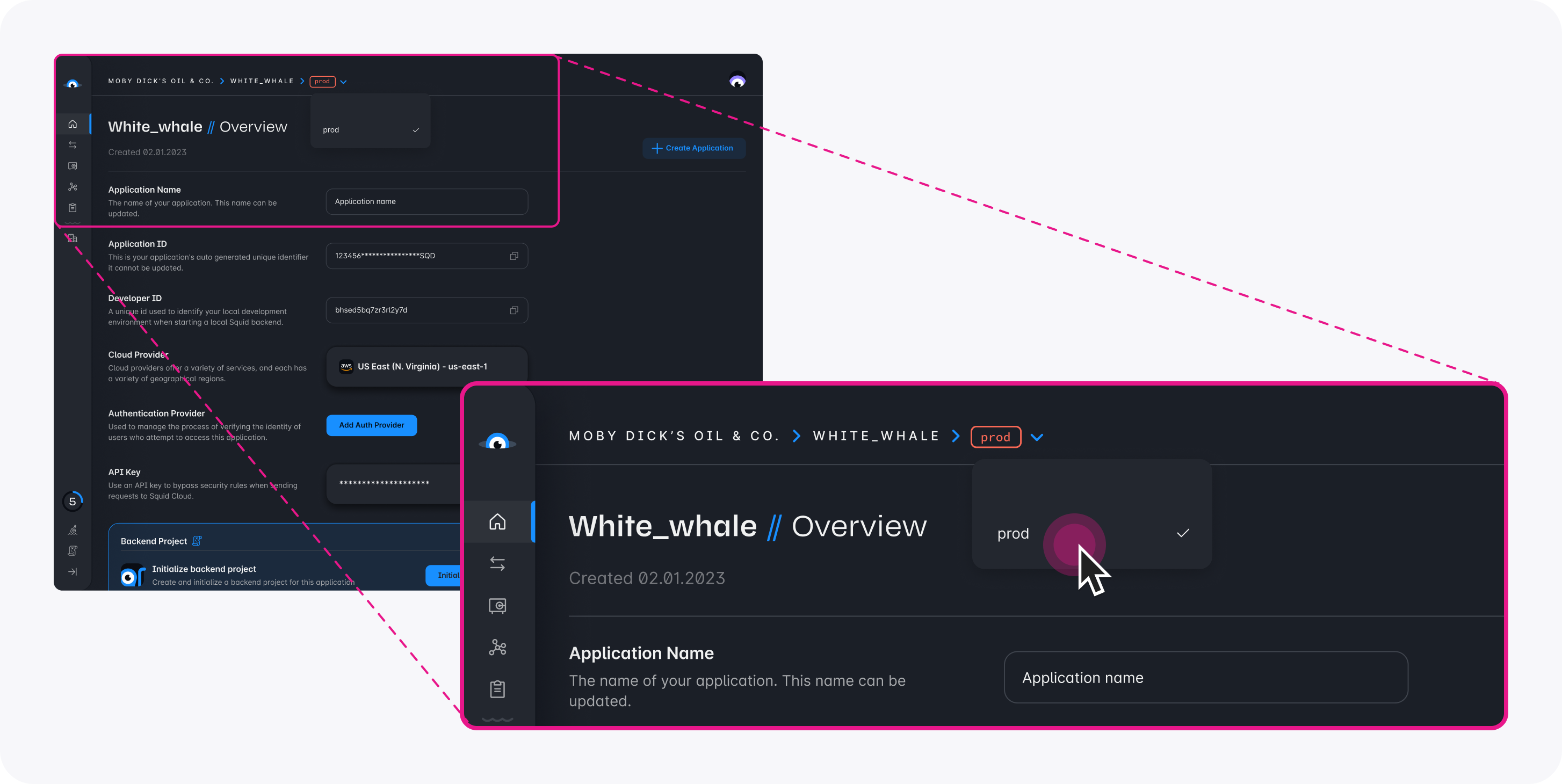
Environments during development
By default, the environmentId and apiKey in your .env file is set to dev, so if you run commands without these flags, the command defaults to the dev environment.
To change your environment in the backend, use the appropriate flags in your Squid CLI commands.
squid deploy # deploys to dev
squid deploy --environmentId prod --apiKey YOUR_PROD_API_KEY # deploys to prod
To change your environment in your app's frontend, use the appropriate environmentId value in your Squid context:
<SquidContextProvider
options={{
appId: 'YOUR_APP_ID',
region: 'YOUR_REGION', // example: 'us-east-1.aws'
environmentId: 'dev', // or 'prod'
}}
>
<App />
</SquidContextProvider>
Key environment variables
Environment variables, also called "envars", are essential for configuring and operating your application in both the development and production environments.
- SQUID_APP_ID: Your unique Squid application identifier. (
--appIdwhen using in the command line) - SQUID_REGION: Specifies the region, such as 'us-east-1.aws'. (
--regionwhen using in the command line) - SQUID_ENVIRONMENT_ID: Indicates the working environment, either 'dev' or 'prod'. (
--environmentIdwhen using in the command line) - SQUID_API_KEY: A distinct key for API access, different for each environment. (
--apiKeywhen using in the command line) - SQUID_DEVELOPER_ID: Necessary for running the Squid backend locally, accessible in the
.envfile or Squid Console. (--squidDeveloperIdwhen using in the command line)
For automated deployments using tools like Netlify or GitHub Actions, we recommended setting these environment variables directly on the deployment machine or within the deployment tool's configuration. This approach ensures better security and management of sensitive information, such as the API Key.
Setting variables on the deployment machine or process also allows for a clear separation between development and production configurations.
Security considerations
Exercise caution with sensitive variables, particularly the API Key. To avoid security risks, it should never be exposed in the client-side code. Always manage such critical information securely, either on the server or within protected environment variables.
Locate envars in the console
For ease of management, you can copy environment variables from the Squid Console. This feature is helpful for setting up your variables accurately for both development and deployment purposes. The Show env vars button in the Squid Console is a convenient tool for accessing these variables.
You may also want to click on the "Create .env file" button to generate a .env file for local development.